What is Shoring in Construction? Top 8 Shoring Methods for Safe and Stable Construction
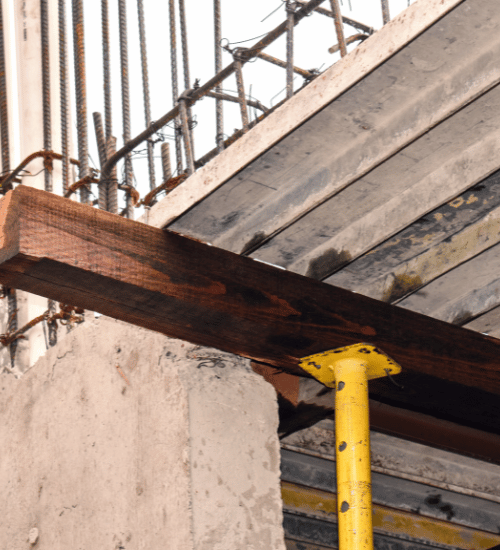

Shoring is a critical process in the construction industry, offering temporary support to stabilize structures, trenches, and excavation sites. Understanding “what is shoring in construction” involves exploring its types, benefits, and when it becomes essential. Whether for a deep excavation project, structural repair, or working on unstable soil, shoring is key to safe, efficient construction. In this guide, we’ll break down what shoring involves, why it’s crucial, the types available, and how to choose the right approach for your project.
What is Shoring in Construction?
Shoring is the process of providing temporary structural support to a building or excavation area to prevent collapses and ensure a safe working environment. This method can include using structures to stabilize soil or existing buildings, particularly when working on a project close to existing structures or in areas where soil stability is a concern. Shoring can be temporary, such as in excavation projects, or semi-permanent, such as when supporting sections of a building during renovations.
By stabilizing a construction site, shoring protects workers, maintains the integrity of nearby structures, and provides safe access for construction activities. With the right shoring method, construction companies can handle complex projects safely and efficiently.
Why Shoring is Essential in Construction Projects
In construction, shoring is essential for safety, compliance, and efficiency. Here’s why it’s so important:
- Preventing Soil and Structural Collapses: Shoring keeps soil from collapsing in excavations, especially in unstable areas.
- Worker Protection: It safeguards workers working near excavations, ensuring they can perform tasks without the threat of sudden structural failure.
- Access to Hazardous Areas: Shoring allows construction crews to safely access parts of a site that might otherwise be too dangerous, such as deep trenches or areas close to unstable walls.
- Maintaining Structural Integrity: When renovating, demolishing, or expanding existing structures, shoring supports walls and foundations, preventing collapses or structural weakening.
In short, shoring is essential whenever there’s a risk of soil movement or structural instability. It not only provides a safer environment but also ensures construction projects can proceed without major disruptions or delays.
Key Benefits of Shoring
Shoring provides several key advantages that enhance the safety, efficiency, and adaptability of a project:
- Enhanced Safety: Shoring stabilizes construction areas, reducing risks to workers and equipment.
- Project Efficiency: By preventing unexpected collapses, shoring minimizes delays and keeps projects on track.
- Flexibility: Shoring systems can adapt to various types of soil and structures, allowing for greater versatility across different construction projects.
- Regulatory Compliance: Shoring helps meet safety regulations, protecting not only the workers but also the project’s long-term viability.
Types of Shoring Methods and Their Applications
Each shoring method has specific benefits, designed to address unique site conditions and project needs. Here’s a look at some of the most effective shoring techniques used in construction:
1. Hydraulic Shoring
- Best For: Fast, adaptable trench support, especially in urban or unstable environments.
- How It Works: Hydraulic cylinders are used to press steel plates against trench walls. This method allows for easy adjustment, making it ideal for quick, temporary support in areas with shifting or unstable soil.
- Advantages: Fast setup and flexibility, great for sites that need shoring in confined spaces or in fast-paced urban projects.
2. Sheet Pile Shoring
- Best For: Coastal, harbor, and flood-prone projects.
- How It Works: Steel sheets with interlocking edges are driven vertically into the ground to create a continuous wall. These sheets form a barrier that prevents soil movement and water ingress, making it ideal for projects near water.
- Advantages: Effective in wet environments, provides excellent soil retention, and minimizes site disturbance.
3. H and I-Beam Shoring (Soldier Pile Shoring)
- Best For: Deep excavations where soil stability is a challenge.
- How It Works: H or I-shaped steel beams are driven into the ground at intervals, with lagging materials like wood or concrete panels filling the gaps between them. This creates a stable wall for deep excavations.
- Advantages: Provides strong lateral support, durable, and adaptable for different depths and soil conditions.
4. Soil Nail Shoring
- Best For: Sloped or unstable terrains where permanent stabilization is needed.
- How It Works: Steel rods, known as “nails,” are driven into the soil at an angle. They are typically grouted in place and can be reinforced with wire mesh or shotcrete (sprayed concrete) to form a solid support system.
- Advantages: Effective for slopes and embankments, offers permanent support, and is ideal for sites with steep, loose soil.
5. Diaphragm Wall Shoring
- Best For: Large-scale deep excavations like basements, tunnels, and retaining walls.
- How It Works: Reinforced concrete walls are built in sections directly within the excavation site, forming a continuous barrier that provides significant structural support.
- Advantages: Highly stable, long-lasting support, suitable for very deep and extensive excavations where space is limited.
6. Contiguous and Secant Pile Shoring
- Best For: Tight urban areas or sites close to existing structures.
- How It Works: Contiguous piles are placed with slight gaps, while secant piles overlap to form an interlocking barrier. Both methods offer strong lateral support in restricted spaces.
- Advantages: Minimizes ground movement, suitable for close-proximity projects, and prevents water ingress with secant piles.
7. Raking Shoring
- Best For: Temporary support for walls or structures during renovations or demolitions.
- How It Works: Angled supports called “rakers” are attached to walls to reinforce them laterally. These rakers transfer the weight from walls to the ground, stabilizing the structure temporarily.
- Advantages: Simple, effective lateral support, ideal for temporary use in construction, demolition, and repair projects.
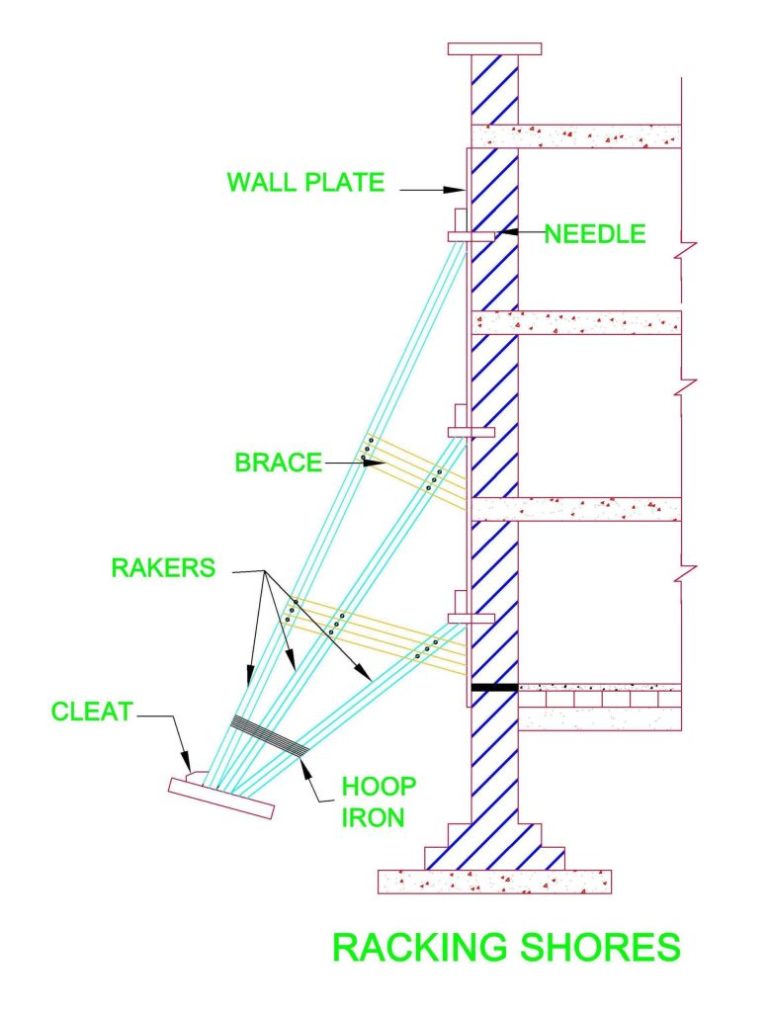
Courtesy: dreamcivil.com
8. Dead Shoring
- Best For: Supporting load-bearing walls during structural modifications or repairs.
- How It Works: Vertical posts and beams are installed beneath the structure to carry its weight. This method is frequently used in renovations where load-bearing walls are being removed or altered.
- Advantages: Provides strong vertical support, ideal for keeping structures stable during extensive interior modifications.
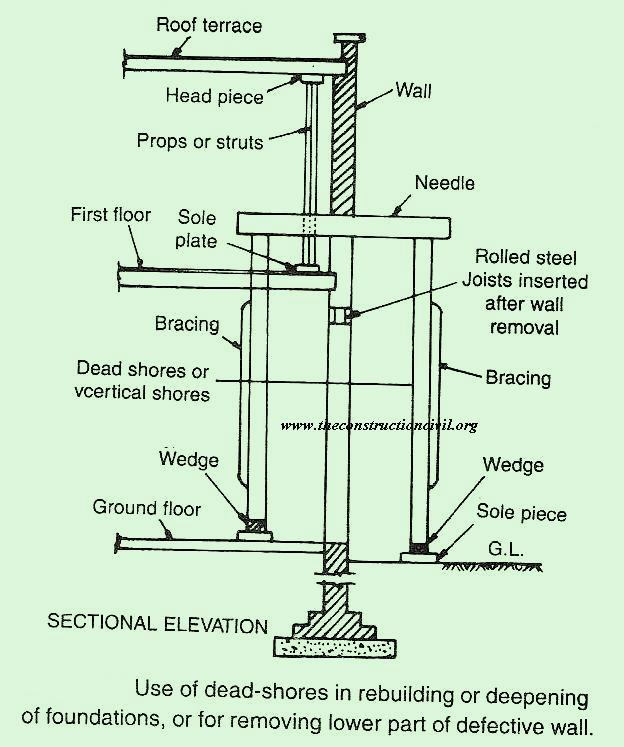
Courtesy: theconstructioncivil.org
Each method offers unique advantages that fit specific project needs, allowing construction teams to stabilize structures effectively while protecting workers and the environment.
Additional Types of Shoring (Beyond Basics)
Some specialized types of shoring may be less common but serve unique needs:
- Timber Shoring: Suitable for smaller or temporary structures, timber shoring is often used in limited spaces or areas where other materials may be too costly.
- Pneumatic Shoring: This uses air compressors to provide support, ideal for excavation sites that require frequent changes in support positioning.
Choosing the Right Shoring Method
Choosing the right shoring method requires careful consideration of factors like:
- Soil Type: Sandy soils might need sheet pile shoring, while hydraulic shoring may be better suited for clay-based soil.
- Excavation Depth and Width: Deeper excavations often need more rigid support structures.
- Environmental Impact: Projects near water sources or protected ecosystems may need methods like sheet pile shoring to minimize disturbance.
- Load-Bearing Needs: Shoring must handle the anticipated structural loads and any additional external forces, such as wind or vehicle traffic.
Evaluating these elements helps ensure that the chosen shoring system is effective, safe, and compliant with regulatory standards.
Key Factors in Shoring Installation
Successful shoring installation requires attention to specific factors:
- Soil Conditions: A thorough soil analysis informs the best shoring method and how it should be installed to handle specific soil behavior.
- Load-Bearing Requirements: Ensuring that the shoring can bear the necessary load keeps the structure stable throughout the project.
- Safety Regulations and Compliance: Meeting industry standards is crucial to protect workers and maintain site integrity. This includes regular inspections and ongoing monitoring of the shoring structures.
The Shoring Process Explained
A successful shoring project typically involves several steps:
- Planning and Design: The initial phase involves site evaluation, choosing the most suitable shoring method, and creating detailed designs that account for structural load, soil conditions, and project requirements.
- Installation: Once designed, the shoring system is carefully positioned and installed as planned.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular inspections ensure that shoring remains effective throughout the project. Any needed adjustments are made to maintain stability. Removal only occurs once the structure is fully self-supporting.
Differences Between Shoring and Scaffolding
Shoring and scaffolding are often confused, but they have distinct roles:
- Shoring: Provides structural support to prevent collapses during construction.
- Scaffolding: Offers a platform for workers to access higher levels and work on different building sections.
While both are critical in construction, understanding this difference is essential to ensure the correct application and safety on-site.
Conclusion
Shoring is fundamental to construction projects that involve deep excavation, structural repairs, or soil stabilization. By selecting and implementing the appropriate shoring method, companies can ensure a safe and stable worksite, prevent delays, and protect workers and nearby assets.
At Broussard Home Services, we bring extensive expertise to each project, ensuring the shoring solution matches the specific needs of the site and meets all safety and regulatory standards.
Contact Broussard Home Services Today!
At Broussard Home Services, we’re committed to supporting your construction needs from foundation to finish. Our team has the experience and tools to ensure your project runs smoothly, safely, and within schedule. Whether it’s an excavation, structural support, or a custom home build, we’re here to help every step of the way.
From initial consultations to project completion, Broussard Home Services takes a personalized approach to every project. Contact us to discuss your project requirements, or fill out our online form to get started. We’re dedicated to bringing your vision to life with safe, reliable, and customized shoring and construction solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the three types of shoring?
The three main types of shoring are raking shoring, flying shoring, and dead shoring. Each is designed to provide specific support based on the structural needs and type of project. - What is the purpose of shoring in construction?
Shoring is used to provide temporary structural support to stabilize soil or buildings during construction, excavation, or renovation. It’s essential for ensuring worker safety and maintaining the stability of nearby structures. - How is shoring done?
Shoring is done by installing temporary supports, like beams or hydraulic props, to stabilize walls or soil. The process involves site assessment, planning, and installation by a professional to ensure effective support. - What is the difference between shoring and a retaining wall?
Shoring provides temporary support for structures and soil during construction, while a retaining wall is a permanent structure designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion in landscaped or sloped areas. - How much does shoring cost?
The average cost of shoring ranges from $500 to $2,000 per linear foot, depending on the method, soil type, and depth. However, it’s best to consult a professional for an accurate quote based on specific project needs. - When is shoring required in a construction project?
Shoring is required during deep excavations, demolition, or renovation where soil stability or structural support is at risk. It is often necessary to comply with safety regulations and ensure project stability.




